Research
Synthesis of Fluorinated Compounds
THE SUCCESS OF FLUORINATION to improve molecular properties has been convincingly demonstrated in a wide range of applications. In many cases, the small and highly electronegative (EN) fluorine atom is introduced following a particular rationale, based on our understanding of the effects of fluorination. In the life sciences area, well-known effects include enhancement of metabolic stability, conformational stabilisation, and modifications of functional group (FG) reactivity, acid/base properties, enhance binding interactions, increaseCNSpenetration or lipophilicity. Importantly, these effects cannot be considered individually as usually a number of properties are influenced simultaneously. For example, fluorination of amines in order to increase their metabolic stability also leads to a decrease in pKa(H), an increase in their lipophilicity, and may induce strong conformational effects. For this reason, the development of new enantioselective methodologies that will deliver enantiopure fluorine compounds (a common moiety in drug candidates) will be of great interest not only for academia but also for chemical industry. In our research group we have developed several methodologies for the enantioselective synthesis of fluorine compounds based on organocatalysis. For example, we developed the first “formal” monomethyl addition to enals, and consequently we developed several cascade reactions based on this concept.[1,2]
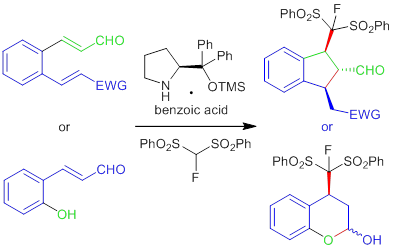
Figure 1: Organocatalytic cascade reaction for the synthesis of fluoro compounds
Related Publications:
1- “Expanding the scope of organocatalytic monofluorination of enals. Enantioselective synthesis of fluoroindanes and Fluorochromanols” B. Wang, Y.-S. Kim, S. Kim, X. Companyó, J. W. Yang, Jing Li , A. Moyano, R. Rios, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 437-446.
2- “Formal Highly Enantioselective Organocatalytic Addition of Fluoromethyl anion to alpha,beta-unsaturated Aldehydes”. A.-N. Alba, X. Companyó, A. Moyano, R. Rios. Chem Eur. J. 2009, 7735-7738.
3- “Organocatalytic Cross Dehydrogenative copling for Synthesis of Fluorinated Compounds” Luke Shirley, Victor Ceban, Marta Meazza and Ramon Rios. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 13-15.
|
|
|

